The Current State of Nigeria’s Real Estate Industry: Growth, Challenges, and Opportunities
Introduction
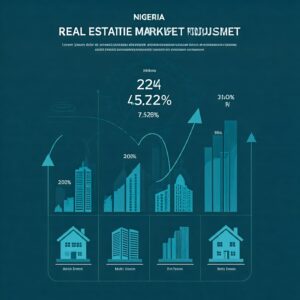
Nigeria’s real estate industry stands at a critical juncture, with a blend of opportunities and obstacles shaping its future trajectory. Despite challenges like infrastructure gaps, a complex regulatory environment, and a housing deficit, the sector is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.52% from 2024 to 2028, reaching an impressive market size of $3.02 trillion. This growth is driven by urbanization, population expansion, and increasing demand for residential and commercial properties. Here’s an in-depth look at the current state, challenges, and growth potential of Nigeria’s real estate industry.
Nigeria Real Estate Industry: Market Size and Potential Growth
The Nigerian real estate industry ranks among Africa’s largest markets, reflecting its pivotal role in the nation’s economy. In 2022, the sector contributed 5.14% to Nigeria’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP), though this figure saw a dip to 3.08% in 2023. This decrease highlights the industry’s dependency on economic conditions and government policies, which can either support or restrict its growth.
Nigeria’s growing population—currently estimated at over 220 million and projected to reach 400 million by 2050—fuels a steady demand for housing and commercial spaces. Rapid urbanisation, especially in cities like Lagos, Abuja, and Port Harcourt, further intensifies the need for real estate development. This urban growth brings both challenges and opportunities for developers aiming to meet the high demand for housing, retail, and office spaces.
Housing Demand and Supply in Nigeria
A significant gap exists between the demand for housing and its supply in Nigeria, exacerbated by rapid population growth and urban migration. The country faces a housing deficit of approximately 28 million units, a number that continues to climb as urban areas expand and rural populations relocate to cities for better job opportunities. High population density in urban centres has driven up the cost of real estate, pushing prices and rents to levels that are increasingly unaffordable for average citizens.
This housing shortfall has created a cycle of rising property prices and increased demand for affordable housing. For real estate developers, this shortage presents an investment opportunity in both low-cost and middle-income housing projects, which could help alleviate the housing crisis and capitalise on the increasing need for residential spaces.
Investment and Financing in Nigeria’s Real Estate
The Nigerian real estate sector continues to be a focal point for both domestic and international investors. Investments span across diverse property types, including residential, commercial, industrial, and retail spaces. With foreign direct investment (FDI) as a key contributor to real estate projects, particularly in urban areas, Nigeria’s market has become increasingly attractive to investors seeking long-term growth.
Several financing options are available to support real estate investments, including bank loans, private equity, mortgages, and government-backed initiatives like the National Housing Fund. These avenues provide funding for property developments and enable developers to pursue large-scale projects, even as economic conditions fluctuate. Access to such financing options also makes it easier for more Nigerians to purchase homes, contributing to a gradual reduction in the housing deficit.
Commercial Real Estate in Nigeria
Commercial real estate is a crucial component of Nigeria’s real estate industry, with Lagos standing out as the country’s commercial epicentre. The city’s booming service sector and concentration of multinational corporations make it a hotspot for commercial real estate development. The demand for office spaces, hotels, retail outlets, and industrial properties has driven steady growth in the commercial sector, creating valuable opportunities for developers and investors.
Despite its promise, the commercial sector is subject to market dynamics such as rental yields, vacancy rates, and economic stability, which can fluctuate in response to external factors. Real estate investors, therefore, must remain adaptable to these market shifts, using careful planning to mitigate risks associated with economic downturns or policy changes.
Regulatory Environment in Nigeria’s Real Estate Industry
Navigating Nigeria’s real estate sector requires a thorough understanding of its regulatory framework, which can be both complex and challenging. Real estate developers face numerous hurdles related to land use laws, property registration, and building permits. The land acquisition process, in particular, is often slow and cumbersome, posing a significant barrier to those looking to enter the market or expand their portfolios.
Investors must also comply with Nigeria’s property taxation policies, which include various levies and fees at both state and federal levels. While these regulations aim to maintain a structured market, they can sometimes deter foreign investors who may be unfamiliar with the country’s regulatory landscape.
Key Challenges in Nigeria’s Real Estate Sector
Housing Deficit and Affordability
The housing deficit remains one of the most significant issues facing the Nigerian real estate industry. The high demand for housing, particularly in urban centres, has led to inflated property prices and rental costs, making affordable housing a challenge for millions of Nigerians. This deficit, coupled with a lack of sufficient low-cost housing options, creates an urgent need for innovative solutions.
Regulatory Complexity
The complexity of Nigeria’s regulatory framework is another pressing concern, as it can delay development projects and discourage investment. Lengthy procedures for acquiring land, coupled with multiple taxation layers, often create bottlenecks that impact the industry’s growth. Simplifying these regulations could encourage more investors to participate in the market.
Economic Fluctuations and Currency Instability
Economic instability and a weakening naira affect the purchasing power of potential buyers, making real estate a more challenging investment for the average Nigerian. Currency devaluation impacts the cost of imported construction materials, driving up overall project costs. Such economic factors emphasize the need for industry players to adopt cost-saving strategies to mitigate these effects.
Opportunities for Growth in Nigeria’s Real Estate Industry
Despite the challenges, Nigeria’s real estate market offers several growth opportunities:
Affordable Housing Projects
There is an increasing demand for affordable housing, particularly among middle- and low-income populations. Developers who focus on creating low-cost housing solutions stand to tap into a high-demand market, addressing the housing deficit while achieving profitable returns.
Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships can serve as a powerful tool to bridge the housing gap. Collaborations between the government and private developers can facilitate access to land, financing, and other resources essential for large-scale housing projects, especially in urban areas.
Sustainable Development and Green Building Practices
As sustainability becomes a global priority, developers in Nigeria have an opportunity to lead the way in eco-friendly building practices. Green buildings can attract environmentally conscious buyers and offer long-term savings through energy efficiency, providing a unique competitive advantage for forward-thinking developers.
Integration of Technology in Real Estate
Technology plays an increasingly crucial role in Nigeria’s real estate industry. From property management software to virtual tours and online property listings, tech solutions enhance transparency, simplify transactions, and improve customer engagement. Tech-savvy developers and agents can use these tools to attract a broader audience and enhance the overall property-buying experience.
Conclusion
The Nigerian real estate industry, while faced with complex challenges, is a sector with promising potential. Rapid urbanisation, population growth, and high demand for housing and commercial properties position the market as a lucrative destination for investors. Developers who can innovate and adapt to market demands, focusing on affordable housing, sustainable development, and tech integration, stand to gain significantly.
With the right policies, government support, and investor confidence, Nigeria’s real estate sector could overcome its current hurdles and experience sustained growth. In navigating the complexities of this industry, stakeholders have the chance to shape a vibrant, resilient real estate market that meets the needs of Nigeria’s expanding population.
Key Points Summary
- Projected Market Size (2024): $2.26 trillion
- Projected Market Size (2028): $3.02 trillion
- CAGR (2024-2028): 7.52%
- Housing Deficit: 28 million units
- Real Estate GDP Contribution (2022): 5.14%
- Real Estate GDP Contribution (2023): 3.08%
- Population: 220 million (projected 400 million by 2050)
- Key Urban Areas: Lagos, Abuja, Port Harcourt
- Commercial Hub: Lagos
FAQs
- What is the current value of Nigeria’s real estate industry?
Nigeria’s real estate market is projected to be worth $2.26 trillion by 2024, growing to $3.02 trillion by 2028. - How does Nigeria’s population impact the housing market?
With over 220 million people and projections to hit 400 million by 2050, Nigeria’s growing population creates a persistent demand for housing. - What are the main challenges in Nigeria’s real estate sector?
The sector faces challenges like a high housing deficit, poor infrastructure, complex regulations, and economic instability. - What are the growth opportunities in Nigeria’s real estate industry?
Key growth areas include affordable housing, public-private partnerships, green building practices, and tech integration. - What role does foreign investment play in Nigeria’s real estate?
Foreign investment provides essential capital for infrastructure projects, enhancing development and supporting market expansion. - How does Lagos contribute to Nigeria’s commercial real estate sector?
Lagos, as Nigeria’s commercial hub, attracts significant commercial real estate investments,